
Or: How to set up a completely private, independent and encrypted communication system in half an hour, using stuff you can buy for under $100.

In this post, we will explore how two people, Alice and Bob, can set up a LoRa mesh communication system for their use that has the following characteristics:
In later parts of this series, we will expand the system to provide these oppertunities to an entire community, and add other mediums like Packet Radio, but for now we will focus on learning the basics by just establishing a Free Communications System between Alice and Bob.
To accomplish this, we will be building a small and simple system based on freely available and Open Source software. To realise our system we will need the following components:
As you might have already guessed, the "magic glue" that acutally makes this entire system possible is Reticulum.
Reticulum is a complete networking stack that was designed to handle challenging situations and requirements like this. Reticulum is an incredibly flexible networking platform, that can use almost anything as a carrier for digital information transfer, and it can automatically form secure mesh networks with very minimal resources, infrastructure and setup.
Please do keep in mind though, that at the time of writing this, Reticulum is still in beta. There might be bugs and security issues that have not yet been discovered. You can keep up with such things, and get updates on the general development and releases, over on the Reticulum GitHub page.
The user-facing software that Alice and Bob will be installing already includes Reticulum, so there is no complicated installation and configuration setups, and getting everything up and running will be quite simple. The requirements are also very minimal, and everything can run on hardware they already have available, be that an old computer, a Raspberry Pi, or an Android phone.
Let's get started.
The first step is to get the LoRa radios prepared and installed. I have written in more length and details about these subjects in other posts on this site (Installing RNode Firmware on Supported Devices and How To Make Your Own RNodes, so this article will just quickly guide you through the basics required to get up and running. For much more information, read the above articles.
First of all, Alice and Bob need to get a compatible piece of radio hardware to use. Had they been living closer to each other, they might have just been able to use WiFi, but they need to cover a distance of more than 7 kilometers, so they decide to go with a couple of LoRa radios.
They take a look at the RNode Firmware Supported Devices List, and decide to go with a couple of LilyGO T-Beam devices. They could have also used others, and they don't need to choose the same device, as long as they are within the same frequency range, all compatible devices work with Reticulum and can communicate with each other, as soon as the RNode Firmware has been installed on them.

Once the devices arrive, it is time to get the firmware installed. For this they will need a computer running some sort of Linux. Alice has a computer with Ubuntu installed, so they decide to use that. Since Python3 came installed as standard with the OS, Alice can go ahead and install the RNode configuration program by simply opening a terminal and typing:
pip install rnodeconf
The above command installs the program they need to flash the LoRa radios with the right firmware. If for some reason Python3 had not already been installed on Alices computer, she would have had to install it first with the command sudo apt install python python-pip.
Now that the firmware installer is ready, it is time to actually get the firmware on to the devices. Alice launches the installer with the following command:
rnodeconf --autoinstall
After this she is greated with an interactive guide that asks a few questions about the device type, grabs the latest firmware files, and installs them onto the device. After repeating with the second device, that is all there is to it, and the LoRa radios are now ready for use with Reticulum.
To get a better signal, Alice mounts her LoRa radio in the attic of her house. She then runs a USB cable from the mounting location to the computer she wants to use for messaging, and plugs the cable into the computer. The LoRa radio is now directly connected to her computer via USB, and receives power from it when the computer is on.
At her computer (running Ubuntu Linux), she installs the Nomad Network program by entering the following command in a terminal:
pip install nomadnet
After a few seconds, Nomad Network and Reticulum is installed and ready to use. She can now run the Nomad Network client by entering the following command:
nomadnet
All required directories and configuration files will now be created, and the client will start up. After a few seconds, Alice will be greeted with a screen like this:
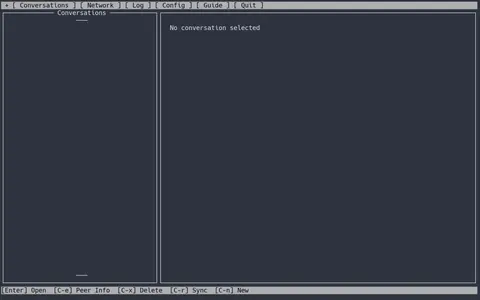
Confirming that everything is installed and working, it is time to add the LoRa radio as an interface that Reticulum can use. To do this, she opens up the Reticulum configuration file (located at ˜/.reticulum/config) in a text editor.
By referring to the RNode LoRa Interface section of the Reticulum Manual, she can just copy-and-paste in a new configuration section for the interface, and edit the radio parameters to her requirements. She ends up with a configuration file that looks like this in it's entirity:
[reticulum]
enable_transport = False
share_instance = Yes
shared_instance_port = 37428
instance_control_port = 37429
panic_on_interface_error = No
[logging]
loglevel = 4
[interfaces]
[[Default Interface]]
type = AutoInterface
interface_enabled = True
[[RNode LoRa Interface]]
type = RNodeInterface
interface_enabled = True
port = /dev/ttyUSB0
frequency = 867200000
bandwidth = 125000
txpower = 7
spreadingfactor = 8
codingrate = 5
Please note that the assignment and use of radio frequency spectrum is completely outside the scope of this exploratory post. Laws and regulations about spectrum use vary greatly around the world, and you will have to do your own research for what frequencies and modes you can use in your location, and what licenses, if any, are required for any given use case.
Alice can now start the Nomad Network client again, and this time around it will initialise and use the LoRa radio installed in her attic. Having completed Alices part of the setup, lets move on to Bobs apartment.
Bob likes his messaging to happen on a handy device like a phone, so he decides to go with the Sideband app instead of Nomad Network. He goes to the download page and installs the APK on his Android phone. He now needs a way to connect to the LoRa radio already running at Alices house to establish communication.
Since he doesn't want to walk around with the LoRa radio constantly dangling by a USB cable from his phone, he decides to set up a Reticulum gateway in his apartment using a Raspberry Pi he had lying around. The RNode LoRa radio will connect via USB to the Raspberry Pi, and the Raspberry Pi will be connected to the WiFi network in his apartment.
This way, any device on his WiFi network (including his Android phone) will be able to route information through the LoRa radio as well. Reticulum takes care of everything automatically, and there is no need to configure addresses, subnet, routing rules or anything.
Both his WiFi router and the Rasperry Pi is powered by a small battery system, so even if the power goes out, the system will be able to stay on for several days on the battery, and indefinitely if he props up a solar panel on his balcony.
Bob installs a fresh copy of Raspberry Pi OS on the small computer, and in the terminal issues the following command to install Reticulum:
pip install rns
In this case, Bob will not be running any user-facing software on the Raspberry Pi itself, so instead he starts Reticulum as a service, by running the rnsd program, to check that everything installed correctly:
rnsd
After a moment, the following output is shown from the rnsd program, signalling that everything is working properly, but that a new, default configuration file has just been created:
[2022-03-26 17:14:05] [Notice] Could not load config file, creating default configuration file...
[2022-03-26 17:14:05] [Notice] Default config file created. Make any necessary changes in /home/bob/.reticulum/config and restart Reticulum if needed.
[2022-03-26 17:14:09] [Notice] Started rnsd version 0.3.3
Bob terminates the rnsd program, and then connects the LoRa radio to the Raspberry Pi with a USB cable. Since he doesn't have any particular access to the roof or attic of the building, he just sticky-tapes the LoRa radio to a window facing in the general direction of Alices house.
He then proceeds to add the same interface configuration to his Reticulum configuration file as Alice did, so that the radio parameters of their respective LoRa radios match each other.
To allow other devices on his network to route through his new Reticulum gateway, he also adds the line enable_transport = yes to his Reticulum config file, so the file in it's entirity looks like this:
[reticulum]
enable_transport = Yes
share_instance = Yes
shared_instance_port = 37428
instance_control_port = 37429
panic_on_interface_error = No
[logging]
loglevel = 4
[interfaces]
[[Default Interface]]
type = AutoInterface
interface_enabled = True
[[RNode LoRa Interface]]
type = RNodeInterface
interface_enabled = True
port = /dev/ttyUSB0
frequency = 867200000
bandwidth = 125000
txpower = 7
spreadingfactor = 8
codingrate = 5
After starting the program again, this time using rnsd -vvv to get more verbose output, he can now see that the LoRa radio is correctly configured and used by Reticulum:
[2022-03-26 18:17:43] [Debug] Bringing up system interfaces...
[2022-03-26 18:17:43] [Verbose] AutoInterface[Default Interface] discovering peers for 1.8 seconds...
[2022-03-26 18:17:45] [Notice] Opening serial port /dev/ttyUSB0...
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Notice] Serial port /dev/ttyUSB0 is now open
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Verbose] Configuring RNode interface...
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Verbose] Wating for radio configuration validation for RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface]...
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Debug] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] Radio reporting frequency is 867.2 MHz
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Debug] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] Radio reporting bandwidth is 125 KHz
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Debug] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] Radio reporting TX power is 7 dBm
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Debug] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] Radio reporting spreading factor is 8
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Debug] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] Radio reporting coding rate is 5
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Verbose] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] On-air bitrate is now 3.1 kbps
[2022-03-26 18:17:47] [Notice] RNodeInterface[RNode LoRa Interface] is configured and powered up
[2022-03-26 18:17:48] [Debug] System interfaces are ready
[2022-03-26 18:17:48] [Verbose] Configuration loaded from /home/bob/.reticulum/config
[2022-03-26 18:17:50] [Verbose] Loaded 0 path table entries from storage
[2022-03-26 18:17:50] [Verbose] Loaded 0 tunnel table entries from storage
[2022-03-26 18:17:50] [Verbose] Transport instance <a5dc367015b30f2d7b59> started
[2022-03-26 18:17:50] [Notice] Started rnsd version 0.3.3
Everything is ready, and when Bob launches the Sideband appplication on his phone, Alice and him will now be able to communicate securely and independently of any other infrastructure.
Both the Nomad Network program and the Sideband application use a cryptographic message delivery system named LXMF, that in turn uses Reticulum for encryption and privacy guarantees. Both Nomad Network and Sideband are LXMF clients.
Much like many different e-mail clients exist, so can many different LXMF clients, and they can all communicate with each other, which is why Alice and Bob can message each other even though they prefer to use very different kinds of user-facing software.
An LXMF addresses consist of 32 hexadecimal characters, and are usually encapsulated in single angle quotation marks like this: <9824f6367015b30f2d7b8a24bc6205d7>.
Nobody controls the allocation of addresses, and since the address space is so huge, and governed by cryptographic principles, you can create as many or as few adresses as you need.
Since you can just create them with freely avaible software, and without any sort of permission from anyone, they are never linked to any personally identifiable information either. They are completely and truly anonymous from the beginning, and you control how much or how little of your identity you associate with them.
For an LXMF address to be reachable for direct-delivery instant messaging on a Reticulum network, it must announce it's public keys on the network. Both Sideband and Nomad Network allows you to send an announce on the network, and both programs can be configured to do so automatically when they start. If you only want to use the system for "email-style" communication (via LXMF propagation nodes), you don't need to send any announces on the network, but to learn how it all works, it is a good idea to just set the programs to automatically announce at start up.
To make sure his public cryptographic key is known by the network, Bob taps the Announce button in the Sideband app:

After a few seconds, Bobs announce shows up in the Announce Stream section of the Nomad Network program on Alices computer:
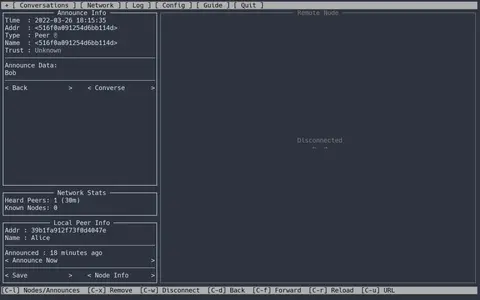
Using the received announce, Alice starts a conversation with Bob. Either one of them could also have started the conversation by manually typing in the others LXMF address in their program, but in many cases it can be convenient to use the announces. Now that everything is ready, they exchange a few messages to test the system. On Bobs Android phone, this looks like this:
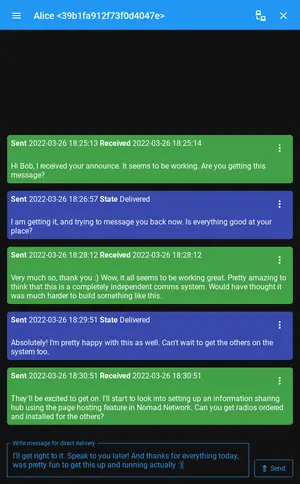
And on Alices computer running Nomad Network, it looks like this:
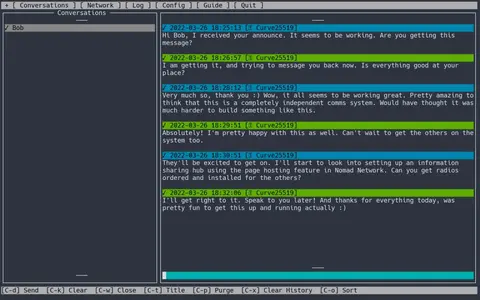
Although pretty useful, what we have explored here does not even begin to scratch the surface of what is possible with Reticulum and associated software. I hope you will find yourself inspired to explore and read deeper into the documentation and available software.
To learn more, take a look at the Learn section.